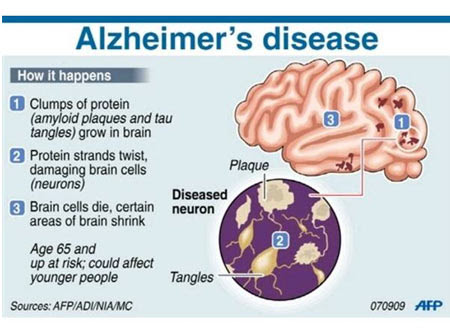
The most common symptom of Alzheimer’s disease is forgetfulness. This condition results from a person’s inability to recall details of events. Oftentimes, people with this condition become frustrated and can lose interest in activities or socializing. These changes in behavior may be difficult for the person to manage. If you think your loved one may be suffering from this disease, it is important to get medical treatment as soon as possible.
Early-stage Alzheimer’s patients may appear healthy, but struggle with everyday tasks. They may be forgetful about some details, but they may also have a sense of something wrong. Some people with the early stage of the disease will retain certain skills, such as walking. They may also experience hallucinations or delusions. They may require help with daily activities. Depending on their health, they may require help with their daily tasks.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms will become more severe. They include disorientation, confusion about time, and mood changes. A person with the disease will lose their memory and become anxious. In addition, they will have problems with walking and may be unsteady on their feet. As the disease worsens, the person may become more irritable and depressed, unable to do things by themselves, and have trouble with language, spelling, and grammar. Additionally, people with the disorder will often have a hard time doing the simplest tasks, such as reading and writing.
The health website https://blognhadat360.com/
says that the most common symptom of Alzheimer’s disease is the inability to recall recent information. This symptom may also be accompanied by problems understanding new information and asking questions. The person may have trouble following conversations and may even end them unexpectedly. This Alzheimer’s symptom can be very distressing for a person, making them feel agitated and frustrated. Some people with this condition will have difficulty walking and may be unsteady on their feet.
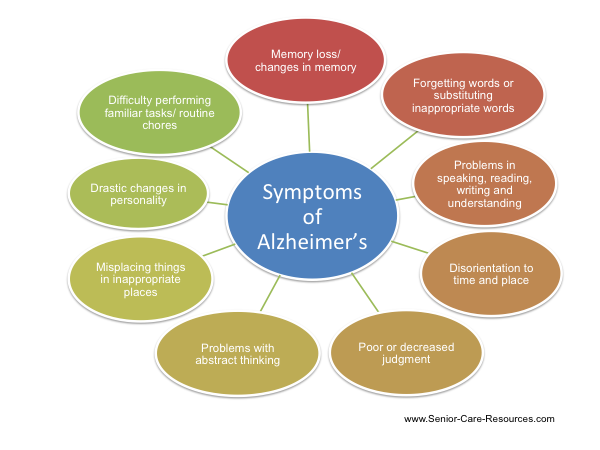
As the disease progresses, a person’s memory deteriorates. This condition can lead to a person’s disorientation, loss of memories, and problems with speech and swallowing. The symptoms of the disease can vary from one person to another. The most common signs include: (a) changes in sleep patterns, b) changes in mood and behavior, and (c) loss of recent and familiar information. Some people may experience all or some of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
The most common symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease include changes in sleep patterns. The person may become irritable and depressed, and he or she may act inappropriately. He or she may also have trouble speaking and may struggle with some tasks. They may repeat things they previously said. Other symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease include seizures and delusions. Oftentimes, they require assistance with everyday activities. Some of the more severe symptoms are the same as those of early-stage Alzheimer’s.
The first stage of the disease is usually mild. The individual may seem to be healthy and do not display many symptoms. However, they may struggle to remember certain details. During this time, the person may become confused, agitated, or in a daze. Sometimes, they may even have trouble speaking or swallowing. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is imperative to see a doctor right away. As the disease advances through the brain, the symptoms will become more severe. Among these are:
The first stage of Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the loss of memory. The person may become depressed, irritable, or frustrated. They may become unable to walk or unsteady on their feet. They may experience difficulty in speaking and repeating previous statements. They may even have trouble spelling and reading their own handwriting. These symptoms are signs that the person has Alzheimer’s disease and is in need of help with everyday activities.
The second stage of the disease begins with the early stage. Its symptoms begin slowly, and gradually become more severe with time. The patient may have trouble following conversations, or may be unable to continue them. The person may have difficulty following conversations or repeating the same words. They may have difficulty naming familiar objects and may put them in unexpected places. They may also lose things they have placed in a different place. The patient may be unable to complete their daily tasks.